We offer you Short Texts at Your Fingertips. Twice each week, we provide teaching ideas around a different type of short text that is easily found in the home, so that no family feels under-resourced. These ideas can integrate into virtually any curriculum and pedagogy, from Workshop to basal. If you are a caregiver, teacher, or curriculum director, these brief but mighty texts and lessons are our way of saying thanks. And our way of giving children authentic and enjoyable reading and writing engagements each day.
Written by Julie Wright & Elizabeth Keim
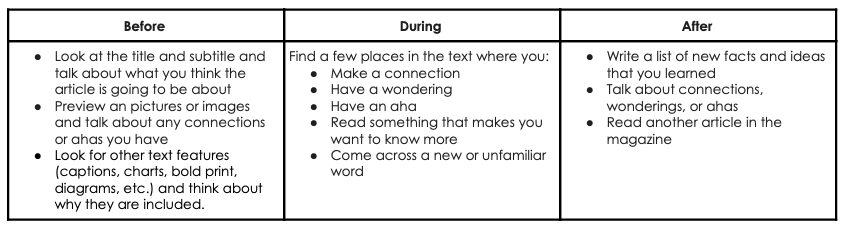
SHORT TEXTS AT YOUR FINGERTIPS: FIELD GUIDES
Field guides are generally used to identify something in nature. There are field guides available for endless subjects: birds, butterflies, trees, mushrooms, rocks and minerals- we could go on and on. A field guide presents lots of information and facts to help teach how to identify a particular species or type within a group. Many of us have at least one field guide on our bookshelf and this is the perfect opportunity to dust it off and use it as a short text! If you don’t have a field guide of your own, there are plenty of online resources to access.
VIDEO
If you’d like to see a short video on how to use field guides to entertain, inform, and inspire watch here.
TRY THIS!
Step 1
Take a look at your bookshelf. Maybe there is a field guide waiting there. If there is more than one, pick the one about the subject most interesting to you. If you don’t have a physical field guide, find one online (see the resource list below). Thumb through the guide and orient yourself to its structure and features. Field guides are designed to be used as a quick reference (possibly in the field). Decide which entry/entries you want to look at more closely.
Some things to consider:
How is this particular guidebook set-up?
Are there sections?
Are the entries organized by type, by color, by region?
Look through the first part of the book. This is usually where the structure of the book is explained and some important facts are provided.
Think about how you might use the guide if you were outside.
Would you want to mark particular pages for easy reference?
Consider how this book is meant to be used.
Does the author intend for it to be read cover to cover?
Step 2
Take a closer look at a specific entry in your field guide.
Here are two different examples:
Here’s what we noticed:
The bird guide on the left uses bold headings to identify characteristics about a bird. It includes a map and it is organized by color (see the oval on the top right).
The bird guide on the right shows similar species together on the same page. Arrows show the most distinguishing marks. On the opposing page there is information about each bird.
Both examples give distinguishing characteristics of the object featured.
Some guides have photographs, some use illustrations.
Step 3
Look for other reading, writing and talking opportunities using this short text type:
Reading Ideas
Compare entries in two different field guides (see above). How are they the same? How are they different?
Look at field guides about two different things (for example birds and mushrooms). What is included in both? What features are particular to the thing being studied?
Explore new vocabulary words. Are there words you have never seen or heard before? How can you find what they mean?
Learn how to use other text features including the Table of Contents, Index and Glossary.
Writing Ideas
Write your own field guide entry for the guide you have. Use the features and structure of the guide to help you.
Write your own field guide about a subject you know well.
You could write about a habitat you know well (e.g., your bedroom, the kitchen).
You could write about a category of things (e.g., your stuffed animals, tools used to draw and write).
Use the field guide to add details to another piece of writing (e.g., include a more detailed description of what a character sees).
Start a “Life List” for the subject in the field guide (e.g., record your personal sightings).
Talking Ideas
Consider who wrote this field guide? How did the author prepare to write this book? How is the preparation different than it would be to write a fiction picture book?
Compare the illustrations to a photograph. What are the advantages to a photograph? What can the illustration show that a photograph cannot?
Discuss who uses field guides and when?
Compare field guides and think about what background knowledge a reader needs to use the guide. Are different guides written for people with different background knowledge?
Step 4
Look for other field guides and explore those too!
FOR MORE RESOURCES, CHECK THESE OUT!
To find a field guide about virtually anything, go online and type “free online field guide about_______”. Here are some examples you might enjoy.
To find more general information about field guides, check this out.
Check this out if you are interested in some fun, simple printable field guides for kids.
For more ideas about creating your own field guide, check this out.
CO-AUTHOR: ELIZABETH KEIM
Elizabeth Keim is a New York City based educator with more than 25 years of experience. She is currently an AIS Reading Teacher/Reading Recovery teacher for a school in Mamaroneck, New York. Previously she taught in District 2 in Manhattan, serving as a classroom teacher, reading specialist, and library teacher. In each of these roles, she knows that, "it is all about finding a text that truly captures a particular reader." She has taught Undergraduate and Graduate level courses at New York University and Bank Street College of Education, as well as workshops for teachers and parents. An avid birder, Elizabeth enjoys her time in Central Park every spring and fall. Her most thrilling sightings to date are: A rare Kirtland's warbler and the tutti frutti colored Summer Tanager.